
Source: NSPS “ Definitions of Surveying and Associated Terms“, used with permission. and sometimes even 60 miles apart from the base line. In many of the surveys made before 1850, standard parallels were run 30, 36. These lines were established to limit the convergence of range lines from the south. Parallel, standard -An auxiliary governing line established along the astronomic parallel initiated at a selected township corner on a principal meridian, usually at intervals of 24 miles from the base line, on which standard township, section, and quarter-section corners are established. The term is applicable to an astronomic as well as a geodetic parallel. Parallel, geographic -A line on the Earth with the same latitude at each point.

In form it is a small circle whose plane is parallel to the plane of the geodetic equator. A geodetic parallel, other than the equator. Parallel, geodetic -A line on an ellipsoid which has the same geodetic latitude at each point. Parallel, celestial -A circle, on the celestial sphere, whose points have the same declination parallel of declination. Auxiliary standard parallels are used in the extension of old surveys and for the control of new surveys. Parallel, auxiliary standard -A new standard parallel or correction line established, when required, for control purposes where original standard parallels or correction lines were placed at intervals of 30 or 36 miles. The astronomic parallel of 0° latitude is called the “astronomic equator” or the “terrestrial equator.” Because the deflection of the vertical is not the same at all points on the Earth, an astronomical parallel is an irregular line, not lying in a single plane. Parallel, astronomic -A line on the surface of the Earth which has the same astronomic latitude at every point. Parallel, arc of -A part of an astronomic or geodetic parallel.
2A circle on the surface of the Earth, parallel to the equator and connecting points of equal latitude, or a circle parallel to the primary great circle of a sphere or ellipsoid also a closed curve approximating such a circle.
1Extending in the same direction and everywhere equidistant. % Each worker must discard all changes to the data dictionary and % close the dictionary when finished with an iteration of the parfor-loopĮnd % Restore default settings that were changed by the function % % Prior to calling cleanupWorkerCache, close the model spmd % Simulate and store simulation output in the nondistributed array % Suppose MODE is a Simulink.Parameter object stored in the data dictionary % Modify the value of MODE SectObj = getSection(dictObj, 'Design Data') % Create objects to interact with dictionary data % You must create these objects for every iteration of the parfor-loopĭictObj = (dd) % Prepare a nondistributed array to contain simulation output

Įnd % Determine the number of times to simulate % Grant each worker in the parallel pool an independent data dictionary % so they can use the data without interference spmd % Define the sweeping values for the variant control (mathematics) one of a set of parallel geometric figures. something having the property of being analogous to something else 3. % For convenience, define names of model and data dictionary an imaginary line around the Earth parallel to the equator 2.


 0 kommentar(er)
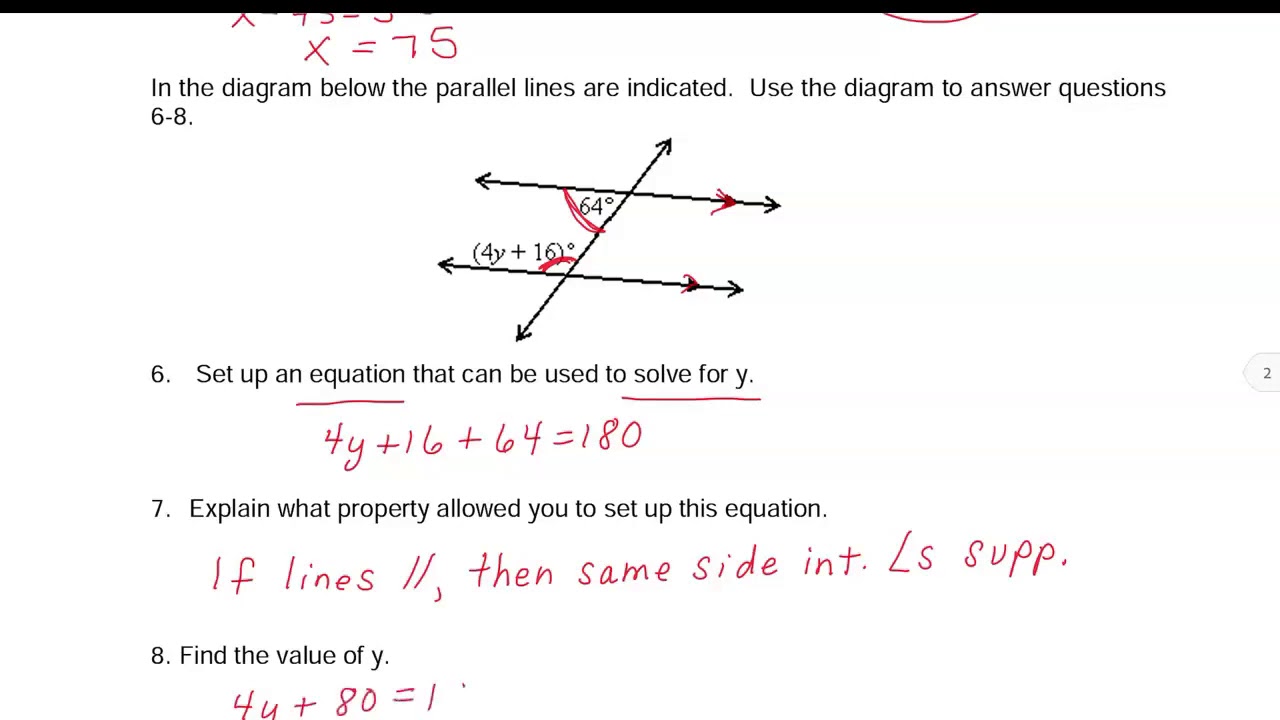
0 kommentar(er)
